- Download Azure Storage Explorer Windows
- Azure File Explorer Download
- Azure Data Explorer
- Azure Storage Explorer Download For Mac
Microsoft Azure Storage Explorer enables you to easily work with Azure Storage data safely and securely on Windows, macOS, and Linux. By following these guidelines, you can ensure your data stays protected.
General
- Always use the latest version of Storage Explorer. Storage Explorer releases may contain security updates. Staying up to date helps ensure general security.
- Only connect to resources you trust. Data that you download from untrusted sources could be malicious, and uploading data to an untrusted source may result in lost or stolen data.
- Use HTTPS whenever possible. Storage Explorer uses HTTPS by default. Some scenarios allow you to use HTTP, but HTTP should be used only as a last resort.
- Ensure only the needed permissions are given to the people who need them. Avoid being overly permissive when granting anyone access to your resources.
- Use caution when executing critical operations. Certain operations, such as delete and overwrite, are irreversible and may cause data loss. Make sure you're working with the correct resources before executing these operations.
Choosing the right authentication method
Download and install Storage Explorer. Connect to an Azure storage account or service. Create a File Share. All files must reside in a file share, which is simply a logical grouping of files. An account can contain an unlimited number of file shares, and each share can store an unlimited number of files. The following steps illustrate how to. Trusted Windows (PC) download Microsoft Azure Storage Explorer 1.8. Virus-free and 100% clean download. Get Microsoft Azure Storage Explorer alternative downloads.
Storage Explorer provides various ways to access your Azure Storage resources. Whatever method you choose, here are our recommendations.
Azure AD authentication
The easiest and most secure way to access your Azure Storage resources is to sign in with your Azure account. Signing in uses Azure AD authentication, which allows you to:
- Give access to specific users and groups.
- Revoke access to specific users and groups at any time.
- Enforce access conditions, such as requiring multi-factor authentication.
We recommend using Azure AD authentication whenever possible.
This section describes the two Azure AD-based technologies that can be used to secure your storage resources.
Azure role-based access control (Azure RBAC)
Azure role-based access control (Azure RBAC) give you fine-grained access control over your Azure resources. Azure roles and permissions can be managed from the Azure portal.
Storage Explorer supports Azure RBAC access to Storage Accounts, Blobs, and Queues. If you need access to File Shares or Tables, you'll need to assign Azure roles that grant permission to list storage account keys.
Access control lists (ACLs)
Access control lists (ACLs) let you control file and folder level access in ADLS Gen2 blob containers. You can manage your ACLs using Storage Explorer.
Shared access signatures (SAS)
If you can't use Azure AD authentication, we recommend using shared access signatures. With shared access signatures, you can:
- Provide anonymous limited access to secure resources.
- Revoke a SAS immediately if generated from a shared access policy (SAP).
However, with shared access signatures, you can't:
- Restrict who can use a SAS. A valid SAS can be used by anyone who has it.
- Revoke a SAS if not generated from a shared access policy (SAP).
When using SAS in Storage Explorer, we recommend the following guidelines:
- Limit the distribution of SAS tokens and URIs. Only distribute SAS tokens and URIs to trusted individuals. Limiting SAS distribution reduces the chance a SAS could be misused.
- Only use SAS tokens and URIs from entities you trust.
- Use shared access policies (SAP) when generating SAS tokens and URIs if possible. A SAS based on a shared access policy is more secure than a bare SAS, because the SAS can be revoked by deleting the SAP.
- Generate tokens with minimal resource access and permissions. Minimal permissions limit the potential damage that could be done if a SAS is misused.
- Generate tokens that are only valid for as long as necessary. A short lifespan is especially important for bare SAS, because there's no way to revoke them once generated.
Important
When sharing SAS tokens and URIs for troubleshooting purposes, such as in service requests or bug reports, always redact at least the signature portion of the SAS.
Storage account keys
Storage account keys grant unrestricted access to the services and resources within a storage account. Office 365 trial mac. For this reason, we recommend limiting the use of keys to access resources in Storage Explorer. Use Azure RBAC features or SAS to provide access instead.
Some Azure roles grant permission to retrieve storage account keys. Individuals with these roles can effectively circumvent permissions granted or denied by Azure RBAC. We recommend not granting this permission unless it's necessary.
Storage Explorer will attempt to use storage account keys, if available, to authenticate requests. You can disable this feature in Settings (Services > Storage Accounts > Disable Usage of Keys). Some features don't support Azure RBAC, such as working with Classic storage accounts. Such features still require keys and are not affected by this setting.
If you must use keys to access your storage resources, we recommend the following guidelines:
- Don't share your account keys with anyone.
- Treat your storage account keys like passwords. If you must make your keys accessible, use secure storage solutions such as Azure Key Vault.
Note
If you believe a storage account key has been shared or distributed by mistake, you can generate new keys for your storage account from the Azure portal.
Public access to blob containers
Storage Explorer allows you to modify the access level of your Azure Blob Storage containers. Non-private blob containers allow anyone anonymous read access to data in those containers.
When enabling public access for a blob container, we recommend the following guidelines:
- Don't enable public access to a blob container that may contain any potentially sensitive data. Make sure your blob container is free of all private data.
- Don't upload any potentially sensitive data to a blob container with Blob or Container access.
Next steps
-->Overview
Azure Blob Storage is a service for storing large amounts of unstructured data, such as text or binary data, that can be accessed from anywhere in the world via HTTP or HTTPS.You can use Blob storage to expose data publicly to the world, or to store application data privately. In this article, you'll learn how to use Storage Explorerto work with blob containers and blobs.
Prerequisites
To complete the steps in this article, you'll need the following:
Create a blob container
All blobs must reside in a blob container, which is simply a logical grouping of blobs. An account can contain an unlimited number of containers, and each container can store an unlimited number of blobs.
The following steps illustrate how to create a blob container within Storage Explorer.
Open Storage Explorer.
In the left pane, expand the storage account within which you wish to create the blob container.
Right-click Blob Containers, and - from the context menu - select Create Blob Container.
A text box will appear below the Blob Containers folder. Enter the name for your blob container. See Create a container for information on rules and restrictions on naming blob containers.
Press Enter when done to create the blob container, or Esc to cancel. Once the blob container has been successfully created, it will be displayed under the Blob Containers folder for the selected storage account.
View a blob container's contents
Blob containers contain blobs and folders (that can also contain blobs).
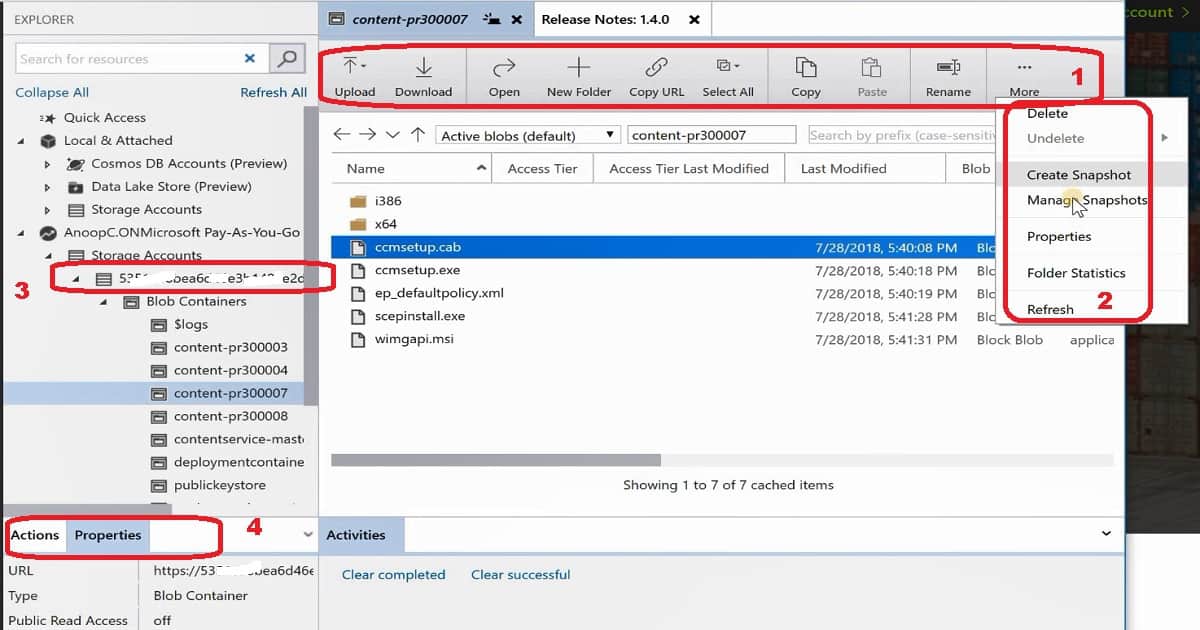
The following steps illustrate how to view the contents of a blob container within Storage Explorer:
Open Storage Explorer.
In the left pane, expand the storage account containing the blob container you wish to view.
Expand the storage account's Blob Containers.
Right-click the blob container you wish to view, and - from the context menu - select Open Blob Container Editor.You can also double-click the blob container you wish to view.
The main pane will display the blob container's contents.
Delete a blob container
Download Azure Storage Explorer Windows
Blob containers can be easily created and deleted as needed. (To see how to delete individual blobs,refer to the section, Managing blobs in a blob container.)
Download xcode 11 for windows. The following steps illustrate how to delete a blob container within Storage Explorer:
Open Storage Explorer.
In the left pane, expand the storage account containing the blob container you wish to view.
Expand the storage account's Blob Containers.
Right-click the blob container you wish to delete, and - from the context menu - select Delete.You can also press Delete to delete the currently selected blob container.
Select Yes to the confirmation dialog.
Copy a blob container
Storage Explorer enables you to copy a blob container to the clipboard, and then paste that blob container into another storage account. (To see how to copy individual blobs,refer to the section, Managing blobs in a blob container.)
The following steps illustrate how to copy a blob container from one storage account to another. Forecast bar.
Open Storage Explorer.
In the left pane, expand the storage account containing the blob container you wish to copy.
Expand the storage account's Blob Containers.
Right-click the blob container you wish to copy, and - from the context menu - select Copy Blob Container.
Right-click the desired 'target' storage account into which you want to paste the blob container, and - from the context menu - select Paste Blob Container.
Get the SAS for a blob container
A shared access signature (SAS) provides delegated access to resources in your storage account.This means that you can grant a client limited permissions to objects in your storage account for a specified period of time and with a specified set of permissions, without having toshare your account access keys.
Azure File Explorer Download
The following steps illustrate how to create a SAS for a blob container:
Open Storage Explorer.
In the left pane, expand the storage account containing the blob container for which you wish to get a SAS.
Expand the storage account's Blob Containers.
Right-click the desired blob container, and - from the context menu - select Get Shared Access Signature.
In the Shared Access Signature dialog, specify the policy, start and expiration dates, time zone, and access levels you want for the resource.
When you're finished specifying the SAS options, select Create.
A second Shared Access Signature dialog will then display that lists the blob container along with the URL and QueryStrings you can use to access the storage resource.Select Copy next to the URL you wish to copy to the clipboard.
When done, select Close.
Manage Access Policies for a blob container
The following steps illustrate how to manage (add and remove) access policies for a blob container:
Open Storage Explorer.
In the left pane, expand the storage account containing the blob container whose access policies you wish to manage.
Expand the storage account's Blob Containers.
Select the desired blob container, and - from the context menu - select Manage Access Policies.
The Access Policies dialog will list any access policies already created for the selected blob container.
Follow these steps depending on the access policy management task:
- Add a new access policy - Select Add. Once generated, the Access Policies dialog will display the newly added access policy (with default settings).
- Edit an access policy - Make any desired edits, and select Save.
- Remove an access policy - Select Remove next to the access policy you wish to remove.

Set the Public Access Level for a blob container
By default, every blob container is set to 'No public access'.
The following steps illustrate how to specify a public access level for a blob container.
Open Storage Explorer.
In the left pane, expand the storage account containing the blob container whose access policies you wish to manage.
Expand the storage account's Blob Containers.
Select the desired blob container, and - from the context menu - select Set Public Access Level.
In the Set Container Public Access Level dialog, specify the desired access level.
Select Apply.
Managing blobs in a blob container
Once you've created a blob container, you can upload a blob to that blob container, download a blob to your local computer, open a blob on your local computer,and much more.
The following steps illustrate how to manage the blobs (and folders) within a blob container.
Azure Data Explorer
Open Storage Explorer.
In the left pane, expand the storage account containing the blob container you wish to manage.
Expand the storage account's Blob Containers.
Double-click the blob container you wish to view.
The main pane will display the blob container's contents.
The main pane will display the blob container's contents.
Follow these steps depending on the task you wish to perform:
Upload files to a blob container
On the main pane's toolbar, select Upload, and then Upload Files from the drop-down menu.
In the Upload files dialog, select the ellipsis (…) button on the right side of the Files text box to select the file(s) you wish to upload.
Specify the type of Blob type. See Create a container for more information.
Optionally, specify a target folder into which the selected file(s) will be uploaded. If the target folder doesn’t exist, it will be created.
Select Upload.
Upload a folder to a blob container
On the main pane's toolbar, select Upload, and then Upload Folder from the drop-down menu.
In the Upload folder dialog, select the ellipsis (…) button on the right side of the Folder text box to select the folder whose contents you wish to upload.
Specify the type of Blob type. See Create a container for more information.
Optionally, specify a target folder into which the selected folder's contents will be uploaded. If the target folder doesn’t exist, it will be created.
Select Upload.
Download a blob to your local computer
- Select the blob you wish to download.
- On the main pane's toolbar, select Download.
- In the Specify where to save the downloaded blob dialog, specify the location where you want the blob downloaded, and the name you wish to give it.
- Select Save.
Open a blob on your local computer
- Select the blob you wish to open.
- On the main pane's toolbar, select Open.
- The blob will be downloaded and opened using the application associated with the blob's underlying file type.
Copy a blob to the clipboard
- Select the blob you wish to copy.
- On the main pane's toolbar, select Copy.
- In the left pane, navigate to another blob container, and double-click it to view it in the main pane.
- On the main pane's toolbar, select Paste to create a copy of the blob.
Delete a blob
- Select the blob you wish to delete.
- On the main pane's toolbar, select Delete.
- Select Yes to the confirmation dialog.
Next steps
Azure Storage Explorer Download For Mac
- View the latest Storage Explorer release notes and videos.
- Learn how to create applications using Azure blobs, tables, queues, and files.
